- Home
- Products
- solution
- Service
- About Us
- Contact
-
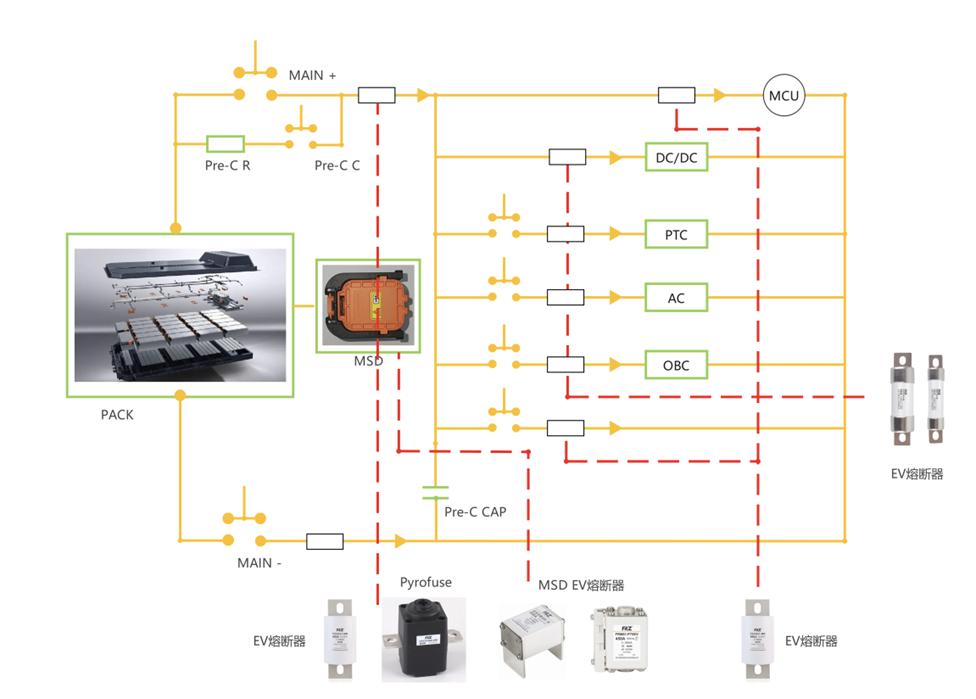
Battery packs are widely used in applications such as electric vehicles (EVs), energy storage systems (ESS), industrial equipment, and power backup systems. As battery capacity and voltage continue to increase, electrical protection becomes a critical safety requirement.
One of the most important protection components inside a battery pack is the battery pack fuse. It plays a key role in preventing damage caused by short circuits, overloads, and abnormal fault conditions.
This article explains what a battery pack fuse is, why it is necessary, and how to choose the right fuse for battery applications.
A battery pack fuse is a protective device installed in series with the battery circuit. Its main function is to interrupt the current automatically when an overcurrent or short circuit occurs, preventing further damage to the battery cells and connected equipment.
Compared with traditional circuit breakers, fuses respond faster and are more reliable in high-fault-current DC systems, which makes them especially suitable for battery applications.Battery packs can deliver extremely high fault currents in a very short time. In the event of a short circuit:
Cables may overheat
Battery cells may swell or catch fire
The entire system may fail
A properly selected battery pack fuse clears the fault quickly and limits the energy released, reducing the risk of thermal runaway.
Overcurrent conditions can permanently damage lithium-ion cells. Once a cell is damaged, it may affect the entire pack.
The fuse isolates the faulty circuit before irreversible damage occurs, extending battery life and improving system reliability.
Many battery systems must comply with international safety standards such as:
IEC 60269 (Low-voltage fuses)
IEC 61851 (EV charging systems)
UL and other regional safety requirements
Using a certified battery pack fuse helps manufacturers meet regulatory and safety compliance requirements.
Battery systems operate in DC, often at high voltages such as:
400V
600V
800V
Up to 1000V DC
The fuse must be specifically designed for DC applications, as DC arc interruption is more demanding than AC.
The current rating must match the normal operating current of the battery pack.
The I²t value determines how much energy the fuse lets through before clearing.
For sensitive battery systems, low I²t fuses are preferred to minimize thermal and mechanical stress on battery cells.
Battery packs can generate very high short-circuit currents. The fuse must have sufficient DC breaking capacity to safely interrupt the maximum possible fault current.
Battery pack design often has limited space. Common installation options include:
Bolt-on fuses
Busbar mounted fuses
Compact cartridge fuses
Mechanical strength and vibration resistance are also important, especially in EV and mobile applications.
Battery pack fuses are widely used in:
Electric vehicles (traction battery protection)
Energy storage systems (ESS / BESS)
Charging stations
Industrial battery systems
UPS and backup power systems
In all these applications, battery safety and reliability depend heavily on correct fuse selection.
When selecting a fuse for battery pack protection, consider the following:
System DC voltage
Continuous operating current
Maximum short-circuit current
Required I²t value
Applicable standards and certifications
Mechanical and environmental conditions
Working with an experienced fuse manufacturer or supplier can help ensure the fuse matches the real application conditions.
A battery pack fuse is not just a simple component—it is a critical safety device that protects batteries, equipment, and users from serious electrical hazards.
As battery systems continue to evolve toward higher power and higher voltage, selecting the correct DC fuse becomes increasingly important for performance, safety, and compliance.

We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience, serve personalized ads or content, and analyze our traffic. By clicking "Accept All", you consent to our use of cookies.